What is inheritance in java?
Inheritance in Java
Inheritance is an important pillar of OOP(Object Oriented Programming). It is the mechanism in java by which one class is allow to inherit the features(fields and methods) of another class.
Important terminology:
- Super Class: The class whose features are inherited is known as super class(or a base class or a parent class).
- Sub Class: The class that inherits the other class is known as sub class(or a derived class, extended class, or child class). The subclass can add its own fields and methods in addition to the super class fields and methods.
- Reusability: Inheritance supports the concept of “reusability”, i.e. when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing class. By doing this, we are reusing the fields and methods of the existing class.
How to use inheritance in Java
The keyword used for inheritance is extends.
Syntax :
Syntax :
class derived-class extends base-class
{
//methods and fields
}
The extends keyword indicates that you are making a new class that derives from an existing class. The meaning of "extends" is to increase the functionality.
In the terminology of Java, a class which is inherited is called a parent or superclass, and the new class is called child or subclass.
Inheritance Example
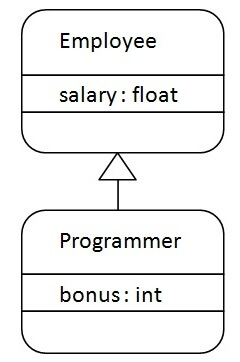
As displayed in the above figure, Programmer is the subclass and Employee is the super class. The relationship between the two classes is Programmer IS-A Employee. It means that Programmer is a type of Employee.
class Employee{
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}
Output:
Programmer salary is:40000.0 Bonus of programmer is:10000
In the above example, Programmer object can access the field of own class as well as of Employee class i.e. code reusability.
Types of Inheritance in Java
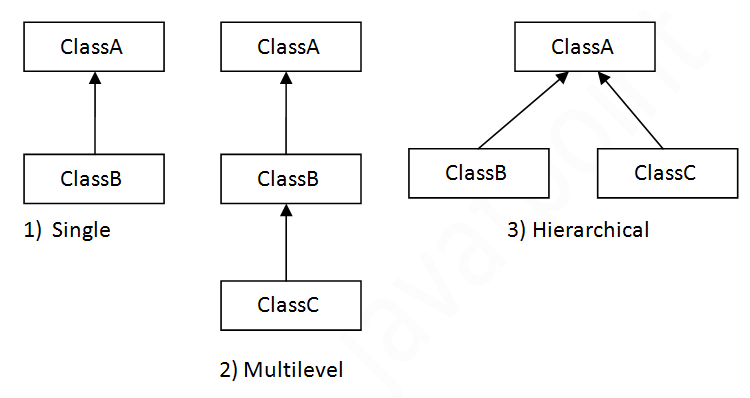
There can be three types of inheritance in java: single, multilevel and hierarchical.
In java programming, multiple and hybrid inheritance is supported through interface only. We will learn about interfaces later.
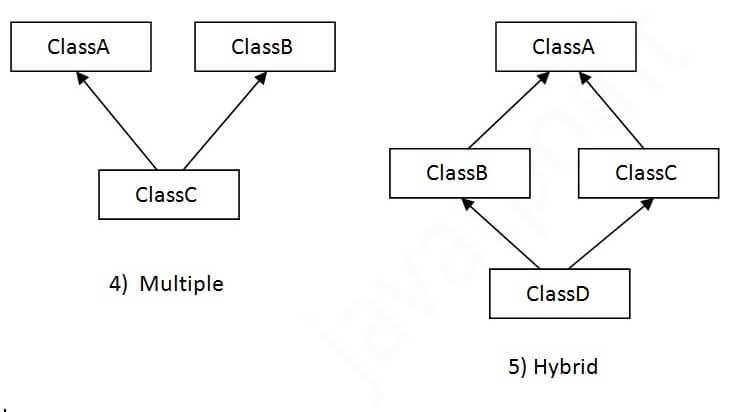
When one class inherits multiple classes, it is known as multiple inheritance. For Example:
Single Inheritance :
In single inheritance, sub classes inherit the features of one super class. In image below, the class A serves as a base class for the derived class B.

void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");}
}
class TestInheritance{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d=new Dog();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
Multilevel Inheritance :
In Multilevel Inheritance, a derived class will be inheriting a base class and as well as the derived class also act as the base class to other class. In below image, the class A serves as a base class for the derived class B, which in turn serves as a base class for the derived class C. In Java, a class cannot directly access the grandparent’s members.

class Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog{
void weep(){System.out.println("weeping...");}
}
class TestInheritance2{
public static void main(String args[]){
BabyDog d=new BabyDog();
d.weep();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog{
void weep(){System.out.println("weeping...");}
}
class TestInheritance2{
public static void main(String args[]){
BabyDog d=new BabyDog();
d.weep();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
Hierarchical Inheritance :
In Hierarchical Inheritance, one class serves as a superclass (base class) for more than one sub class.In below image, the class A serves as a base class for the derived class B,C and D.

void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
void meow(){System.out.println("meowing...");}
}
class TestInheritance3{
public static void main(String args[]){
Cat c=new Cat();
c.meow();
c.eat();
//c.bark();//C.T.Error
}
}
Multiple Inheritance (Through Interfaces) :
In Multiple inheritance ,one class can have more than one super class and inherit features from all parent classes. Please note that Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes. In java, we can achieve multiple inheritance only through Interfaces. In image below, Class C is derived from interface A and B.

// Java program to illustrate the
// concept of Multiple inheritance
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
interface one
{
public void print_geek();
}
interface two
{
public void print_for();
}
interface three extends one,two
{
public void print_geek();
}
class child implements three
{
@Override
public void print_geek() {
System.out.println("Geeks");
}
public void print_for()
{
System.out.println("for");
}
}
// Drived class
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
child c = new child();
c.print_geek();
c.print_for();
c.print_geek();
}
}
Hybrid Inheritance(Through Interfaces) :


Comments
Post a Comment